Satellite images show Ukrainian security agency drones destroying four launchers and two radars of the Russian S-400 Triumph air defense missile system
2025年12月5日Elon Musk boasts, China silently dries up, satellite warfare situation quietly changes
2025年12月5日
The aerospace industry, as a typical knowledge and technology intensive and high value-added industry, was initially led by the government in its development. The purpose of conducting space exploration was mainly to serve the needs of national security and military operations. Therefore, the aerospace industry has always been regarded as the focal point of great power strategic games and an exclusive competitive field at the national level. The development level of the aerospace industry is a reflection of a country’s comprehensive strength and national defense strength.
In recent years, driven by a new round of global industrial revolution, the development of the global aerospace industry has entered a new stage of great development and transformation. The development model of relying solely on the state has changed, and commercial aerospace has become a new and important force to promote the rapid development of the aerospace industry. The globally renowned aerospace technology company SpaceX has achieved landmark achievements in space history with its liquid fuel rocket launch and reusable rocket technology. Its new business models, such as Starlink broadband (private network communication), satellite launch (satellite outsourcing), and commercial manned spaceflight and delivery, have expanded the space industry’s new application scenarios. Represented by SpaceX, commercial aviation companies are driving the rapid development of the world’s aerospace industry through technological innovation and new business models.
The rapid development of global commercial aerospace has driven unprecedented prosperity in the aerospace industry, attracting widespread attention from all sectors of society and demonstrating the enormous vitality and infinite energy contained in the commercialization of the aerospace industry. With the opening of the space industry to private capital in 2015, China’s commercial space industry began to enter the initial and exploratory stage. To this day, China has produced commercial achievements in multiple fields of the aerospace industry, and the research and application services of many private enterprises have turned commercial aerospace blueprints into reality.It can be foreseen that in the new era of space exploration, where the journey is like a sea of stars, China’s commercial space development has enormous room for imagination.
01 Development History of China’s Commercial Aerospace Industry
Table 1: Review of Major Events in China’s Commercial Aerospace Development
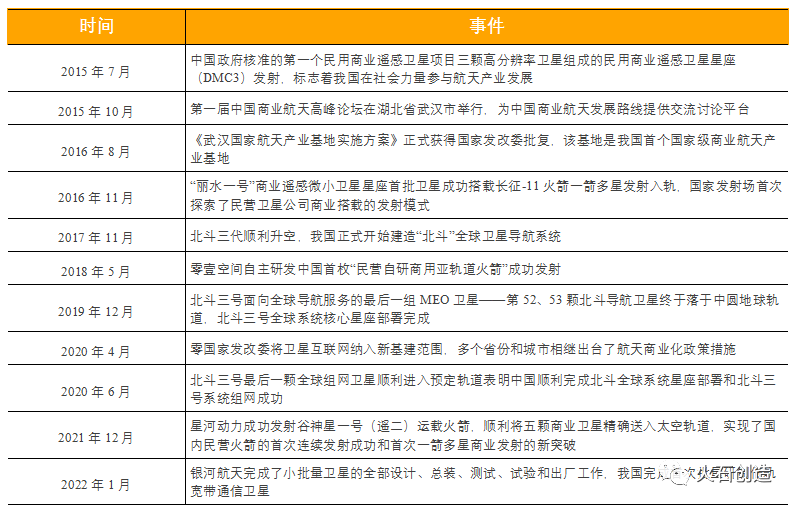
Data source: Huoshi Creation. According to publicly available information, since 2014, the government has issued a series of relevant documents aimed at promoting diversified investment and industrial applications in the aerospace industry. The aerospace industry, which has long been monopolized by the state, has opened its doors to private capital for the first time. 2015 is widely regarded as the first year of China’s commercial aerospace development. In July 2015, China’s first civilian commercial remote sensing satellite constellation (DMC3), “Beijing-2”, was successfully launched, marking a significant development of China’s social forces participating in the aerospace industry. Under the guidance of commercial aerospace related support policies, development planning outlines, extensive participation of social capital, continuous breakthroughs in core technologies, and the country’s strategy of incorporating satellite Internet into the “new infrastructure”, China’s commercial aerospace industry is in the ascendant. There has been a large wave of aerospace enterprises in the market joining the wave of commercial aerospace development, participating in the competition of various aerospace tracks, and the development pattern of the commercial aerospace industry has begun to take shape.
02 Market size of China’s commercial aerospace industry
Since its inception in 2015, China’s commercial aerospace industry has shown a trend of annual growth, with output value increasing from 376.4 billion yuan in 2015 to 1020.2 billion yuan in 2020, with an average annual growth rate of 22%. In 2020, the commercial aerospace market size exceeded one trillion yuan for the first time. With the continuous development of digital technology and the continuous expansion of application fields, the success of Beidou Global Navigation System constellation networking, and the inclusion of satellite Internet in the national “new infrastructure” category in 2020, the demand for commercial launch will grow rapidly, the degree of aerospace industrialization will be greatly improved, and the commercial aerospace market will continue to accelerate expansion. It is expected that the size of China’s commercial aerospace market will reach 2.406 trillion yuan by 2024.
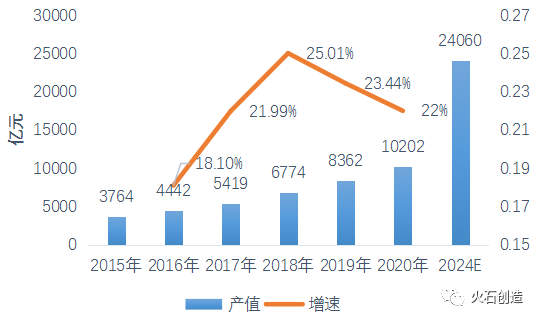
Figure 1: Scale and Forecast of China’s Commercial Aerospace Market
Data source: Firestone Creation. Compiled from publicly available information
03 Development Pattern of Chinese Commercial Aerospace Enterprises
From the perspective of enterprise types, they can be divided into national teams and private commercial aerospace enterprises based on the nature of their property rights.The national team is represented by participants from the two major state-owned enterprise groups, Aerospace Science and Technology and Aerospace Science and Industry. Most of them have national research institutes and state-owned backgrounds, and play the role of the main force and pillar in satellite launch, satellite manufacturing, and satellite applications related to major aerospace projects that require a large amount of funding and technical support. For example, in 2019, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation released a plan for the development and launch of the “Dragon” series of carrier rockets, mainly aimed at meeting China’s growing demand for commercial payload to orbit. Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation and Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation have respectively proposed the “Hongyan” and “Hongyun” low orbit satellite communication constellation plans, aiming to complete the construction of a domestic low orbit satellite communication system by the end of 2023, which will effectively drive the expansion of ground equipment and communication system operation output scale. In the field of satellite applications with higher marketization, richer application scenarios, and wider market space, private commercial aerospace enterprises have a higher level of participation and perform better. Overall, China’s business presents a pattern of diversified market entities participating in competition, led by large central enterprises and with the participation of multiple private enterprises, jointly leading the vigorous development of China’s aerospace industry.
In terms of the number of enterprises, the number of commercial aerospace companies in China has grown rapidly in recent years.Since 2015, with the influx of a large amount of capital, a large number of start-up private aerospace enterprises have emerged, and market entities have continued to expand. According to relevant statistics, the number of registered commercial aerospace enterprises in China increased from 141 at the end of 2018 to 194 at the end of 2019, representing a growth rate of 37.6%. By the end of 2020, there were 313 registered commercial aerospace companies in China, an increase of 61.3% compared to 2019. From 2018 to 2020, the number of enterprises doubled within two years.
From the perspective of industry segmentation,As of the end of 2020, there were 84 commercial aerospace enterprises registered in the field of satellite manufacturing, 47 in the field of satellite launch, and 48 in the field of satellite operation,The largest number of enterprises in the field of satellite applicationsReaching 134 households. Compared with 2018, the number of enterprises in the field of satellite applications has increased significantly, which is closely related to the rapid development of satellite Internet technology, the multi-directional application of low orbit satellite communications, and the wide access of Beidou navigation technology to the field of people’s livelihood.
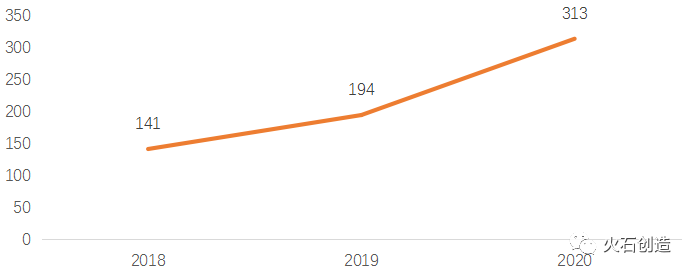
Figure 2: Number of Commercial Aerospace Enterprises in China from 2018 to 2020
Data source: Firestone Creation. Compiled from publicly available information
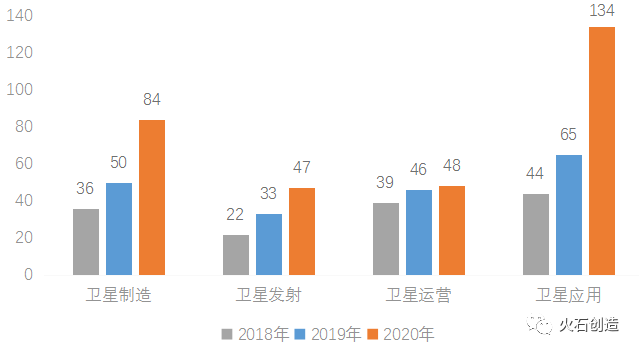
Figure 3: Number of Commercial Aerospace Enterprises in China from 2018 to 2020
Data source: Firestone Creation. Compiled from publicly available information
03 Analysis of the Commercial Aerospace Industry Chain
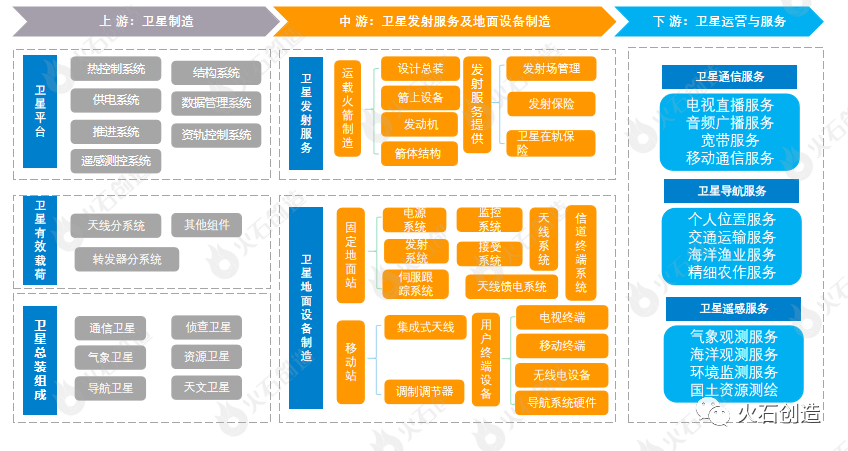
Figure 4: Commercial Aerospace Industry Chain Source: Huoshi Creation According to publicly available information
The entire commercial aerospace industry chain is divided into three links: upstream, midstream, and downstream. The upstream of the industrial chain is satellite manufacturing; The midstream of the industry chain includes satellite launch services and ground equipment manufacturing, among which satellite launch services mainly involve the carrier rocket manufacturing industry chain; The downstream of the industrial chain is mainly satellite operation and services.
(1) The satellite manufacturing process mainly consists of three parts: satellite platform, satellite payload, and satellite final assembly and integration.Among them, the satellite payload refers to the specific instruments, equipment, or subsystems used to execute the satellite after it enters orbit, and the type of payload varies depending on the type of mission; A satellite platform refers to the basic universal module of a satellite, which includes thermal control, structure, power supply, data management, propulsion, orbit control, remote sensing measurement and control, and other subsystems, except for the payload or payload compartment. Finally, the various parts of the satellite will undergo final assembly and integration testing to produce satellite products with different application fields.
Worldwide, typical commercial aerospace companies represented by SpaceX, OneWeb, and Telesat are planning to build large low orbit satellite communication constellations.China’s low orbit satellite constellation plan has been launched, and the three major communication satellite constellations of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation’s Hongyan Plan, China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation’s Hongyun Project, and Xingyun Project are all planned to be deployed in low orbit. The first low orbit satellite IoT constellation “Tianqi Constellation” developed and operated by State Grid Corporation of China will be fully deployed this year. LEO constellations realize the commercial networking of the entire constellation through hundreds of thousands of small satellites (usually satellites below 1000 kg). The plans for multiple LEO Internet constellations around the world are being promoted, and tens of thousands of satellites will fly into space in the future. The booming development of low orbit satellite constellations has driven a significant increase in the demand for small satellites, and the mass production of small satellites with characteristics such as small size, low launch cost, and short production cycle has become a trend in satellite manufacturing. State owned capital represented by China’s satellites and aerospace technology, as well as commercial satellite private enterprises represented by Micro Nano Star, Galaxy Aerospace, and Tianyi Research Institute, will focus on low orbit communication satellite constellations and promote the large-scale deployment of small and micro satellite industries.
(2) Satellite launch services and ground equipment manufacturingThe midstream of the aerospace industry is divided into satellite launch services and ground equipment manufacturing, with carrier rockets being the main provider of commercial satellite launches.
1. Manufacturing of Launch VehiclesThe effective payloads of artificial satellites, manned spacecraft, space probes, etc. are carried into orbit by carrier rockets, so commercial rocket manufacturing is a key link in satellite launch services. Its main components include on-board equipment, engines, rocket body structure, and rocket assembly integration. The development and production of commercial launch vehicles have the characteristics of long cycles, high technological barriers, and large capital requirements, so the number of enterprises in the industry is relatively small. The two national aerospace teams, Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation and Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, occupy a large market share in the commercial launch field. The “Fast Boat” series under Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation and the “Long March” series under Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation meet the launch needs of the vast majority of commercial satellites. Commercial launch vehicles developed by large commercial rocket companies such as Zero One Space, Star Glory, and Blue Arrow Aerospace have been successfully launched in recent years.
How to reduce costs is a key focus of commercial rocket development, and commercial aerospace companies will focus on the following three aspects for cost control.
(1) One arrow, multiple stars.The “one rocket, multiple satellites” technology refers to the use of a single carrier rocket to simultaneously or in batches release several satellites into their respective orbits, which can significantly reduce launch costs and improve launch efficiency. SpaceX, a US commercial space company, has launched up to 143 small satellites using the Falcon 9 carrier rocket, setting a record for the world’s largest number of single satellite launches. At present, China has only reached the level of launching 20 satellites with one rocket, and there is still huge room for improvement.
(2) Rocket recovery and reuse technology.Rocket recovery and reuse technology refers to the ability to partially or completely recover components from spacecraft and reuse them. By recycling and reusing rocket stages, the cost of rocket launch can be significantly reduced. Currently, the only reusable carrier rocket in the world is SpaceX’s Falcon 9. China is exploring the technology of rocket reuse. In 2019, the Long March 4B carrier rocket successfully implemented a sub stage landing zone control flight demonstration and verification, laying a solid foundation for the development of vertical takeoff and landing reusable carrier rockets in the future.
(3) Liquid engine technology.Power engineering is the core of launch vehicles, and space rocket engines can be divided into liquid engines and solid engines. Compared to solid rocket engines, liquid rocket engines have larger tonnage, higher combustion efficiency, and depth variable thrust capabilities, making it easier for rockets to achieve recycling and reuse functions. Therefore, variable thrust rocket engines are an inevitable trend for achieving reusable launch vehicles, and the development of liquid engines is a long-term advantageous choice for launch vehicle companies. Private rocket manufacturers in China, such as Blue Arrow Aerospace, Kyushu Cloud Arrow, and Aerospace Propulsion, are actively laying out liquid engine products.
2. Manufacturing of satellite ground equipmentSatellite ground equipment is composed of fixed ground stations, mobile stations and user terminals. It is the terminal equipment of satellite Internet, satellite communication operation, satellite navigation system and other industrial links, and occupies a large share of the downstream application market. The White Paper on China’s Aerospace in 2016 emphasizes the construction of an integrated information network consisting of space-based systems such as high orbit broadband and low orbit mobile satellites, as well as ground-based systems such as gateway stations; The comprehensive completion of the Beidou-3 global navigation system in 2020 has driven the continuous promotion of China’s satellite ground equipment; The 14th Five Year Plan of our country also clearly proposes to build a high-speed ubiquitous, integrated, interconnected, secure and efficient information infrastructure. It can be foreseen that with the continuous promotion of national policies and the continuous development of downstream satellite application markets, the scale of China’s satellite ground equipment market will further expand.
(3) Satellite Operations and ServicesSatellite operation and service are the application links of artificial satellites, and the applications of various artificial satellites are mainly concentrated in the three major fields of communication, navigation, and remote sensing.
1. Satellite communicationSatellite communication refers to the use of artificial satellites as relay stations to amplify electromagnetic waves emitted by Earth stations and then send them back to another Earth station, achieving wireless communication between two or more Earth stations. Compared with ground communication, satellite communication has advantages such as wide coverage area, less susceptibility to ground conditions, and more abundant spectrum resources available. Satellite communication technology is widely used in commercial fields such as broadcasting and television, broadband services, etc.
High definition, especially ultra high definition programs, require a large amount of satellite communication capacity. High throughput satellites provide several times, even tens of times, or even hundreds of times more capacity than traditional satellites through high-level frequency reuse and use, with the advantages of higher bandwidth, faster speed, and more portable receivers. In 2022, the construction of the Hongyun Constellation, Hongyan Constellation, and Galaxy Aerospace Constellation will complete phased deployment, providing low bandwidth and low rate narrowband IoT satellite constellations in low Earth orbit. High throughput satellites in low Earth orbit will become the infrastructure of future space network networks, promoting China’s entry into the era of low Earth orbit communication. At that time, the scale of services such as video calls and high-definition video on demand will continue to expand. At the same time, high-throughput satellites have large bandwidth capacity, strong anti-interference ability, and easy installation of terminals, which can meet various application needs such as maritime communication, airborne communication, and land vehicle communication. In the future, satellite communication will be more popular in sea, land, and air applications.
2. Satellite navigationSatellite navigation refers to the technology of using navigation satellites to navigate and locate ground, ocean, air, and space users. The main global satellite navigation systems include the Global Positioning System (GPS) of the United States, the Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS) of Russia, the Beidou Satellite Navigation System (BDS) of China, and the Galileo positioning system (GALILEO) of the European Union.
In 2020, with the successful launch of the last networked satellite of China’s Beidou-3 global satellite navigation system in Xichang, the comprehensive construction of China’s independently built and operated global satellite navigation system was completed. With the completion of the Beidou system, satellite navigation will become one of the main downstream application areas in the commercial aerospace industry. The Beidou satellite navigation system has been widely used in productive activities and government services such as transportation, agriculture, forestry, fisheries, maritime distress search and rescue, urban governance, and has also entered into mass consumption and livelihood fields such as e-commerce, mobile intelligent terminal manufacturing, and smart wearable devices. In the future, the Beidou Navigation System will develop towards high precision and systematization, and integrate with 5G, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and big data to provide accurate spatiotemporal information for new technological infrastructure such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and blockchain, expanding a broader market space. With the continuous updates of satellite navigation systems, the continuous improvement of comprehensive performance, and the upgrading and transformation brought about by industrial integration, the civilian market of satellite navigation industry will continue to maintain a high-speed growth trend.
3. Satellite remote sensingSatellite remote sensing is the use of artificial satellites to perceive the properties and spatial distribution characteristics of targets through the propagation and reception of electromagnetic waves (including light waves), and analyze and process them to achieve observation and monitoring of the Earth.
In practical applications, satellite remote sensing is mainly used for national defense and government in the fields of land, emergency security, and meteorology. With technological progress, cost reduction, and the increasing demand for high-quality geospatial data in various industries, remote sensing satellites have rapidly emerged as commercial applications in precision agriculture, forest pest monitoring, environmental monitoring, and other areas. Under the promotion of commercialization of remote sensing satellites, the number of launches of commercial remote sensing satellites in China has significantly increased, and the number of market participants has gradually increased. China’s privately-owned listed company, Orbit, has started establishing a remote sensing satellite constellation called “Zhuhai No.1”. The commercial remote sensing satellite constellation “Jilin-1” built by Changguang Satellite has 41 in orbit, making it the largest optical remote sensing satellite constellation in China at present.

Figure 5: Atlas of Commercial Aerospace Enterprises in China Source: Huoshi Creation Compiled from Public Information
05 Summary
Against the backdrop of global space commercialization, the space field has become a new high ground of competition, and the era of great space exploration has begun. Since 2015, with the support of policies and capital, China’s aerospace industry has developed rapidly, and the industrial development pattern has been initially established. At present, with the introduction of satellite Internet into new infrastructure, the deployment plans of various types of satellite constellations of commercial aerospace state-owned enterprises and private enterprises are gradually completed, and the industrialization process of satellite manufacturing and application is further accelerated. The 14th Five Year Plan of our country points out that building a globally covered and efficient communication, navigation, and remote sensing space infrastructure system, constructing commercial space launch sites, and further promoting the development of commercial space. Driven by policies and business environment, multiple cities including Beijing, Xi’an, Shenzhen, Shanghai, Wuhan, Ningbo, and Guangzhou have successively introduced policy plans in the field of commercial aerospace, accelerating the layout of commercial aerospace.
During the 13th Five Year Plan period, China’s commercial aerospace industry made a leap from scratch and is now entering an important period of catching up and development. On the national level, the key needs are to optimize the top-level planning and design of aerospace, and promote the opening and sharing of aerospace manufacturing infrastructure; In terms of commercial aerospace enterprises, it is necessary to strengthen their technological innovation capabilities and develop feasible business models for users and markets. Through the joint efforts of government and enterprises, the commercial aerospace industry will continue to write new glories in this new journey!
